What Is Bandwidth Management?
Learn about bandwidth management and bandwidth control.
What Is Bandwidth Management?
Bandwidth Management Definition
Bandwidth management occurs after businesses or organizations measure how bandwidth is used on their network.
Bandwidth is the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over a network connection within a given period or how much information a network can handle at once. Generally, bandwidth is measured in bits per second (bps), megabits per second (Mbps), or gigabits per second (Gbps). High bandwidth enables faster data transmission, which leads to better performance for streaming, downloading, video conferencing, and more.
Note that bandwidth shouldn’t be confused with speed. While both can impact overall performance, bandwidth refers to a network’s capacity to transmit data, while speed indicates how quickly data can be uploaded, downloaded, or otherwise delivered to devices.
A higher bandwidth usually means faster network connection speeds. This is especially true when multiple devices or users are connected to the same network. A higher network bandwidth reduces the likelihood of congestion, meaning users can have fast, smooth, and reliable performance for high-bandwidth activities, such as large file transfers and video streaming.
Bandwidth management is the process of controlling and optimizing how bandwidth is allocated and used across a network. For this, organizations must closely monitor network traffic, set priorities for specific types of traffic, limit usage when needed, and allocate resources effectively, among other actions, to reduce latency, prevent congestion, boost efficiency, improve performance, and ultimately enhance the overall user experience. Often, organizations turn to bandwidth management software to efficiently monitor and optimize how data transfer is handled on the network.
How Does Bandwidth Control Work?
Bandwidth control involves monitoring, prioritizing, and regulating network traffic to optimize bandwidth usage and improve overall performance and user experience. More specifically, bandwidth control involves:
- Identifying high-bandwidth-consuming devices, users, and processes: One of the first steps to controlling bandwidth is identifying which devices and activities are using the most bandwidth. Common culprits include video streaming and large file downloads. By pinpointing which areas are consuming the most bandwidth and discovering potential bottlenecks, network administrators can make adjustments to ensure all critical processes and applications have the resources they need. For example, some bandwidth management tools enable organizations to control bandwidth based on the time of day or define the amount of bandwidth granted to an application or task, either as an exact amount or a percentage.
- Using traffic shapers: Traffic shapers, or packet shapers, can help limit how much bandwidth- and speed-specific data streams can be accessed. This means IT teams can restrict how much bandwidth specific applications or individual users can access, allowing critical applications and other high-priority traffic to operate smoothly without being impacted by lower-priority activities. For example, a business might use traffic shapers to limit bandwidth for non-essential activities like streaming services or social media browsing to prioritize more important business processes, such as vital cloud-based applications and video conferencing technology.
- Performing quality of service checking: Many organizations use quality of service (QoS) checking alongside traffic shapers. While the goal of traffic shaping is to limit low-priority traffic on the network, QoS checking ensures crucial network traffic is prioritized. With the help of QoS features and settings, IT teams can allocate or reserve more bandwidth to critical applications and deprioritize the less essential ones to help increase the reliability and performance of these high-priority applications, even during periods of heavy network usage.
- Using a proxy cache: By storing copies of frequently accessed pages and content locally, a proxy cache reduces the need to retrieve data repeatedly from external servers. After all, the content is already in the cache. This can minimize the bandwidth required to load websites and stream videos, helping alleviate network congestion. Plus, proxy caching can speed up access times for users, enabling them to retrieve regularly visited content faster.
- Restricting streaming service access: Streaming services, such as YouTube, Netflix, and Spotify, are a common culprit behind bandwidth congestion. These platforms consume large amounts of data—which shoot up when streaming videos in 4K or high-definition. That’s why many network administrators limit access to streaming platforms during peak usage hours as part of their bandwidth control strategy. They may reduce streaming quality to standard definition to conserve bandwidth while still allowing some access or completely block streaming service access for specific users or devices.
- Limiting VoIP usage: Since VoIP consumes considerable network bandwidth, restricting its usage can help free resources for other, more vital applications. Network administrators might choose to implement policies to limit VoIP calls during peak usage hours or reduce call quality to save bandwidth. Additionally, it’s possible to prioritize VoIP traffic for essential users and business-critical communications.
- Centralizing application updates: Another effective bandwidth control method, centralizing application updates, involves downloading updates to a central server one time. Then, IT teams can distribute them locally to devices within the network. Not only can this minimize redundant traffic and reduce bandwidth consumption during application updates but also accelerate the updating process.
- Using advanced anti-malware tools: It’s also a good idea to use powerful anti-malware tools to protect the network from malicious software that can consume excessive bandwidth or disrupt network performance. Botnets, spyware, and other forms of malware can generate significant amounts of traffic, which consumes much bandwidth, slows down the entire network, and ultimately impacts operations. Advanced anti-malware solutions can assist IT teams in detecting, blocking, and removing these cyber threats, helping prevent unnecessary bandwidth consumption.
Why Is Bandwidth Control Important?
Bandwidth control is essential to businesses and organizations of all sizes because it can help reduce network bottlenecks and boost overall system performance. Overburdened and overworked networks can lead to slow connections, dropped communications, reduced productivity, and poor performance.
Bandwidth control can impact an organization’s ability to function efficiently by ensuring critical applications and services are prioritized and operate smoothly. With proper bandwidth control techniques, organizations may improve performance for various tasks, including VoIP services, video conferencing streams, online backups, cloud service access, file uploads and downloads, email communications, and real-time collaboration tools.
By managing bandwidth, organizations can ensure critical applications and services receive the resources they need to provide users with a high-quality experience. Bandwidth control can help prevent network congestion, lower the risk of service disruptions, avoid bandwidth hogging, and provide consistent, reliable performance. Plus, proper bandwidth management can help with resource allocation optimization, enabling organizations to scale and prevent over-provisioning their network resources.
Bandwidth control can also be an essential factor in reducing malicious activity. For example, since bandwidth control can limit the amount of bandwidth available to certain users or types of traffic, it can help mitigate the impact of distributed denial of service attacks, which overwhelm a network by flooding it with excessive traffic to cause slowdowns or outages. As a result, organizations can keep their critical services operational and maintain business continuity.
Additionally, proper bandwidth control can help IT teams avoid costly downtime. By preventing network congestion and prioritizing essential traffic, services, and applications, businesses can avoid interruptions that may lead to lost revenue, decreased customer satisfaction, or reputational damage that can lower profits.
What Does Bandwidth Management Software Do?
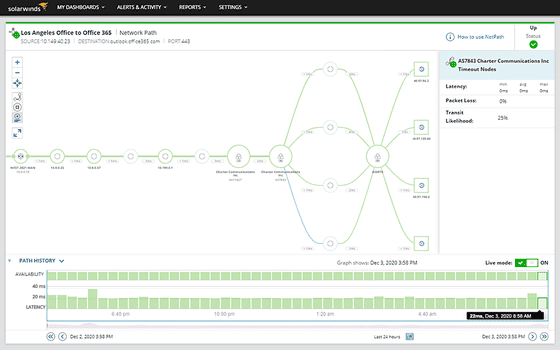
Bandwidth management software empowers organizations to monitor, control, analyze, and allocate network bandwidth effectively. By providing IT teams with a unified platform, it delivers actionable insights into which users, services, or applications are consuming the most bandwidth. This facilitates informed decisions about resource allocation to optimize network performance. With these tools, network administrators can identify high-bandwidth users and activities, limit non-essential traffic, and prioritize critical applications and services, ensuring a seamless and efficient network experience.
Most bandwidth management software comes equipped with advanced features that simplify network oversight while providing users with valuable insights and control over bandwidth usage. These features often include traffic shaping, real-time monitoring, and QoS management, which work together to reduce congestion, minimize disruptions, enhance productivity, and streamline operations. By leveraging bandwidth management software with these features, organizations can find it easier to maintain a reliable and optimized network that supports their current operational needs and adapts as their business and demands change.
SolarWinds® Observability Self-Hosted, previously known as Hybrid Cloud Observability, is a powerful network bandwidth management and control tool that can help users analyze traffic patterns and identify bandwidth hogs to optimize bandwidth usage and avoid bottlenecks. It offers on-premises and cloud observability, allowing organizations to automate, observe, visualize, and remediate their applications, databases, networks, infrastructure components, and more from a single location. Users can easily identify the root cause of bandwidth bottlenecks, receive timely alerts based on customized bandwidth thresholds, and determine which endpoints consume the most network bandwidth.
What Is Bandwidth Management?
Bandwidth Management Definition
Bandwidth management occurs after businesses or organizations measure how bandwidth is used on their network.
Bandwidth is the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over a network connection within a given period or how much information a network can handle at once. Generally, bandwidth is measured in bits per second (bps), megabits per second (Mbps), or gigabits per second (Gbps). High bandwidth enables faster data transmission, which leads to better performance for streaming, downloading, video conferencing, and more.
Note that bandwidth shouldn’t be confused with speed. While both can impact overall performance, bandwidth refers to a network’s capacity to transmit data, while speed indicates how quickly data can be uploaded, downloaded, or otherwise delivered to devices.
A higher bandwidth usually means faster network connection speeds. This is especially true when multiple devices or users are connected to the same network. A higher network bandwidth reduces the likelihood of congestion, meaning users can have fast, smooth, and reliable performance for high-bandwidth activities, such as large file transfers and video streaming.
Bandwidth management is the process of controlling and optimizing how bandwidth is allocated and used across a network. For this, organizations must closely monitor network traffic, set priorities for specific types of traffic, limit usage when needed, and allocate resources effectively, among other actions, to reduce latency, prevent congestion, boost efficiency, improve performance, and ultimately enhance the overall user experience. Often, organizations turn to bandwidth management software to efficiently monitor and optimize how data transfer is handled on the network.
How Does Bandwidth Control Work?
Bandwidth control involves monitoring, prioritizing, and regulating network traffic to optimize bandwidth usage and improve overall performance and user experience. More specifically, bandwidth control involves:
- Identifying high-bandwidth-consuming devices, users, and processes: One of the first steps to controlling bandwidth is identifying which devices and activities are using the most bandwidth. Common culprits include video streaming and large file downloads. By pinpointing which areas are consuming the most bandwidth and discovering potential bottlenecks, network administrators can make adjustments to ensure all critical processes and applications have the resources they need. For example, some bandwidth management tools enable organizations to control bandwidth based on the time of day or define the amount of bandwidth granted to an application or task, either as an exact amount or a percentage.
- Using traffic shapers: Traffic shapers, or packet shapers, can help limit how much bandwidth- and speed-specific data streams can be accessed. This means IT teams can restrict how much bandwidth specific applications or individual users can access, allowing critical applications and other high-priority traffic to operate smoothly without being impacted by lower-priority activities. For example, a business might use traffic shapers to limit bandwidth for non-essential activities like streaming services or social media browsing to prioritize more important business processes, such as vital cloud-based applications and video conferencing technology.
- Performing quality of service checking: Many organizations use quality of service (QoS) checking alongside traffic shapers. While the goal of traffic shaping is to limit low-priority traffic on the network, QoS checking ensures crucial network traffic is prioritized. With the help of QoS features and settings, IT teams can allocate or reserve more bandwidth to critical applications and deprioritize the less essential ones to help increase the reliability and performance of these high-priority applications, even during periods of heavy network usage.
- Using a proxy cache: By storing copies of frequently accessed pages and content locally, a proxy cache reduces the need to retrieve data repeatedly from external servers. After all, the content is already in the cache. This can minimize the bandwidth required to load websites and stream videos, helping alleviate network congestion. Plus, proxy caching can speed up access times for users, enabling them to retrieve regularly visited content faster.
- Restricting streaming service access: Streaming services, such as YouTube, Netflix, and Spotify, are a common culprit behind bandwidth congestion. These platforms consume large amounts of data—which shoot up when streaming videos in 4K or high-definition. That’s why many network administrators limit access to streaming platforms during peak usage hours as part of their bandwidth control strategy. They may reduce streaming quality to standard definition to conserve bandwidth while still allowing some access or completely block streaming service access for specific users or devices.
- Limiting VoIP usage: Since VoIP consumes considerable network bandwidth, restricting its usage can help free resources for other, more vital applications. Network administrators might choose to implement policies to limit VoIP calls during peak usage hours or reduce call quality to save bandwidth. Additionally, it’s possible to prioritize VoIP traffic for essential users and business-critical communications.
- Centralizing application updates: Another effective bandwidth control method, centralizing application updates, involves downloading updates to a central server one time. Then, IT teams can distribute them locally to devices within the network. Not only can this minimize redundant traffic and reduce bandwidth consumption during application updates but also accelerate the updating process.
- Using advanced anti-malware tools: It’s also a good idea to use powerful anti-malware tools to protect the network from malicious software that can consume excessive bandwidth or disrupt network performance. Botnets, spyware, and other forms of malware can generate significant amounts of traffic, which consumes much bandwidth, slows down the entire network, and ultimately impacts operations. Advanced anti-malware solutions can assist IT teams in detecting, blocking, and removing these cyber threats, helping prevent unnecessary bandwidth consumption.
Why Is Bandwidth Control Important?
Bandwidth control is essential to businesses and organizations of all sizes because it can help reduce network bottlenecks and boost overall system performance. Overburdened and overworked networks can lead to slow connections, dropped communications, reduced productivity, and poor performance.
Bandwidth control can impact an organization’s ability to function efficiently by ensuring critical applications and services are prioritized and operate smoothly. With proper bandwidth control techniques, organizations may improve performance for various tasks, including VoIP services, video conferencing streams, online backups, cloud service access, file uploads and downloads, email communications, and real-time collaboration tools.
By managing bandwidth, organizations can ensure critical applications and services receive the resources they need to provide users with a high-quality experience. Bandwidth control can help prevent network congestion, lower the risk of service disruptions, avoid bandwidth hogging, and provide consistent, reliable performance. Plus, proper bandwidth management can help with resource allocation optimization, enabling organizations to scale and prevent over-provisioning their network resources.
Bandwidth control can also be an essential factor in reducing malicious activity. For example, since bandwidth control can limit the amount of bandwidth available to certain users or types of traffic, it can help mitigate the impact of distributed denial of service attacks, which overwhelm a network by flooding it with excessive traffic to cause slowdowns or outages. As a result, organizations can keep their critical services operational and maintain business continuity.
Additionally, proper bandwidth control can help IT teams avoid costly downtime. By preventing network congestion and prioritizing essential traffic, services, and applications, businesses can avoid interruptions that may lead to lost revenue, decreased customer satisfaction, or reputational damage that can lower profits.
What Does Bandwidth Management Software Do?

Bandwidth management software empowers organizations to monitor, control, analyze, and allocate network bandwidth effectively. By providing IT teams with a unified platform, it delivers actionable insights into which users, services, or applications are consuming the most bandwidth. This facilitates informed decisions about resource allocation to optimize network performance. With these tools, network administrators can identify high-bandwidth users and activities, limit non-essential traffic, and prioritize critical applications and services, ensuring a seamless and efficient network experience.
Most bandwidth management software comes equipped with advanced features that simplify network oversight while providing users with valuable insights and control over bandwidth usage. These features often include traffic shaping, real-time monitoring, and QoS management, which work together to reduce congestion, minimize disruptions, enhance productivity, and streamline operations. By leveraging bandwidth management software with these features, organizations can find it easier to maintain a reliable and optimized network that supports their current operational needs and adapts as their business and demands change.
SolarWinds® Observability Self-Hosted, previously known as Hybrid Cloud Observability, is a powerful network bandwidth management and control tool that can help users analyze traffic patterns and identify bandwidth hogs to optimize bandwidth usage and avoid bottlenecks. It offers on-premises and cloud observability, allowing organizations to automate, observe, visualize, and remediate their applications, databases, networks, infrastructure components, and more from a single location. Users can easily identify the root cause of bandwidth bottlenecks, receive timely alerts based on customized bandwidth thresholds, and determine which endpoints consume the most network bandwidth.
Visualize, observe, remediate, and automate your environment with a solution built to ensure availability and drive actionable insights.